
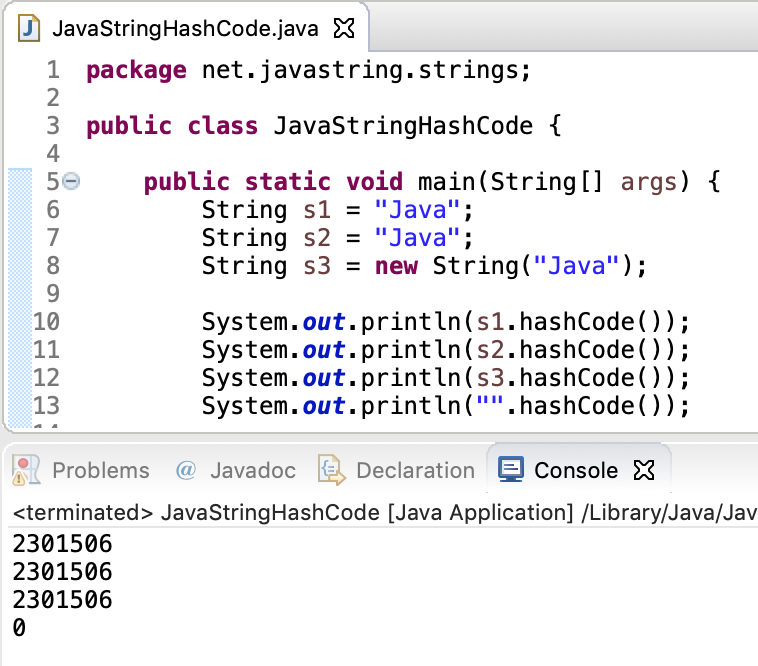
String sf1=String.format(“Number is %x”, 23) Ĭonversions denoted by upper-case character (i.e. ‘B’, ‘H’, ‘S’, ‘C’, ‘X’, ‘E’, ‘G’, ‘A’, and ‘T’) are the same as those for the corresponding lower-case conversion characters only difference is that the result is converted to upper case according to the rules of the locale. String.format(“Local time: %tT”, Calendar.getInstance()) These are prefix for date and time conversion characters Results in platform specific line separator Results in hex string based on the output of hashCode() method Results in decimal number in computerized scientific notationįormat is based on computerized scientific notation or decimal format, depending on the precision and the value after rounding. String.format(“value is %b”,”a”.equals(“a”)) īyte, Byte, short, Short, int, Integer, long, Long and BigInteger If arg is a boolean or Boolean, then the result is the string returned by String.valueOf(arg). If the argument arg is null, then the result is “false”.

The result is a hexadecimal representation of the floating point number Lets take a look at the available conversion specifiers along with their examples. As the specifiers are the ones that tells how the conversion has to be processed and where to add the arguments in the text. Java String Format conversion specifiers are the ones which plays a major role in String formatting.
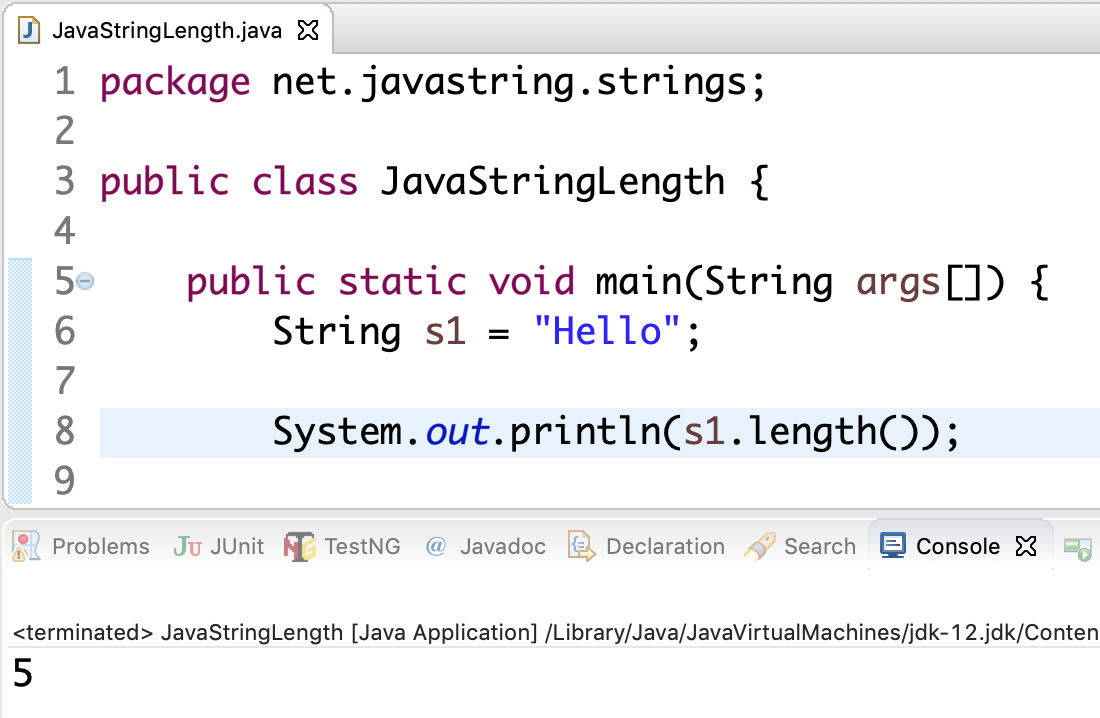
We can use formatter with StringBuffer and StringBuilder as well.įormatter.format("value is %f",32.33434) Java String Fromatter with StringBuffer and StringBuilder ("Error occurred with cause: %s", ex.getMessage()) ("The result of %d / %d = %d", num1,num2,result) Also to provide a custom error messages on console. (): Mostly used to print an error on console.("The result of %d * %d = %d", num1,num2,result) (): Most commonly used for printing on console for debugging purpose or for printing an output on the screen.The examples for the above mentioned methods are provided below. Printf() and format() methods behave in the same way. In order to get formatted strings on console we need to use the following methods. There are situation and scenarios when we would like to have formatted string appear on the console the usage of it can vary from debugging to better readable code. If the locale is not specified in String.format() method, it uses default locale by calling Locale.getDefault() method. The format method also uses locale for formatting a string. It contains a format specifier “%s” which tells how the argument should be processed and where it will be placed in the output. In the example above, “My name is %s” is the format string. The String.format() method returns the formatted String based on the format String and the arguments provided to the method. String Formatter benefit is clearly visible where the format string is read from a property file.With String concatenation we have to do the conversion between different objects to strings.If formatted string is long then string concatenation cause readability issues.String concatenation is a costly affair.The Array declaration is of two types, either we can specify the size of the Array or without specifying the size of the Array. The searching and sorting operation can be performed on the String Array.The String Array can be iterated using the for loop.The elements can be added to a String Array after declaring it.It can be initialized either at the time of declaration or by populating the values after the declaration.It can be declared by the two methods by specifying the size or without specifying the size.The main method in Java is also an String Array.Ĭonsider the below points about the String Array: The first element will take place in Index 0, and the 2 nd element will take place in Index 1, and so on.

It is an index-based data structure, which starts from the 0 th position. In Array, only a fixed set of elements can be stored. The String Array works similarly to other data types of Array. Generally, a string is an immutable object, which means the value of the string can not be changed. It uses a contiguous memory location to store the elements.Ī String Array is an Array of a fixed number of String values. It is one of the most used data structure by programmers due to its efficient and productive nature The Array is a collection of similar data type elements. An Array is an essential and most used data structure in Java.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
